Advanced Wound Care Market Future Prospects
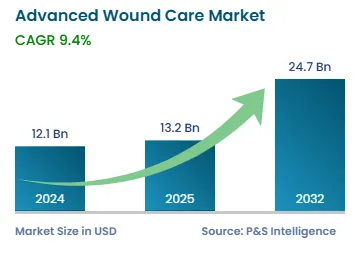
The global advanced wound care market size stands at USD 12.1 billion in 2024, which is expected to reach USD 24.7 billion by 2032, advancing at a CAGR of 9.4% during 2025–2032. This is predominantly due to the rising incidence of surgical and other types of injuries all over the world. In addition, the improving medical safety standards are expected to aid the domain growth during the forecast period.
The technological advancements in the field of wound care are resulting in the launch of innovative and more-effective products. Additionally, an increase in the cases of burns is snowballing the adoption of these products, as is the global increase in the incidence of diabetes and obesity.
Various activities, such as conferences and workshops, are hosted by different associations, such as the Wound Healing Institute Australia (WHIA), Wound Care Education Institute (WCEI), and National Alliance of Wound Care (NAWC), to create awareness among people regarding the treatment of external injuries, best practices, and improvements in the existing methods.
Further, the prominent players are coming forth with innovative products to offer better treatment options to patients. Traditional products, such as gauzes, plasters, sponges, and wadding, have limited effectiveness compared to the advanced ones. The modern products have a higher absorption capacity, which is important for preventing wound seepage; apart from a high oxygen exchange and moisture retaining potential. With the increasing popularity of such products, their adoption in modern healthcare settings is burgeoning.
Moreover, technological advancements have enabled the introduction of advanced dressing, wound therapy devices, and active care products. For instance, Procellera, offered by Vomaris Wound Care Inc., is an antimicrobial dressing designed to enhance the body’s ability to utilize its electrical energy to increase the healing process. In addition, the Chytoform chitosan-based gelling technology by Alicia Diagnostics Inc. consists of gelling fibers derived from crustacean shells. These products are designed for early recovery, easy utilization, higher comfort levels, inflammation reduction, and infection prevention.
The increase in the road accident count across the globe is expected to increase the demand for such products to heal the injuries. Wounds formed during accidents are exposed to debris, soil, bodily fluids, and microbes. In addition, the tissue lost during road accidents increases the time for healing, thus leading to a high demand for collagen, foam, and combination dressings with antimicrobials.
The market for advanced wound care products is extremely fragmented, with several small and large manufacturers present; therefore, the rivalry is expected to become fiercer over the coming period. Additionally, to strengthen their product portfolios, the key players are involving themselves in R&D, collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions. For instance, Smith & Nephew plc has developed the PICO 14 single-use NPWT system and dressing in the U.S.