Report Code: 12241 | Available Format: PDF | Pages: 86
Japan Micromobility Market Research Report: By Type (E-Scooters, E-Bikes, E-mopeds, E-Pods, Bikes, Scooters), Model (First- and Last-Mile, Multimodal), Sharing System (Docked, Dockless) - Industry Analysis and Growth Forecast to 2030
- Report Code: 12241
- Available Format: PDF
- Pages: 86
- Report Description
- Table of Contents
- Market Segmentation
- Request Free Sample
Market Overview
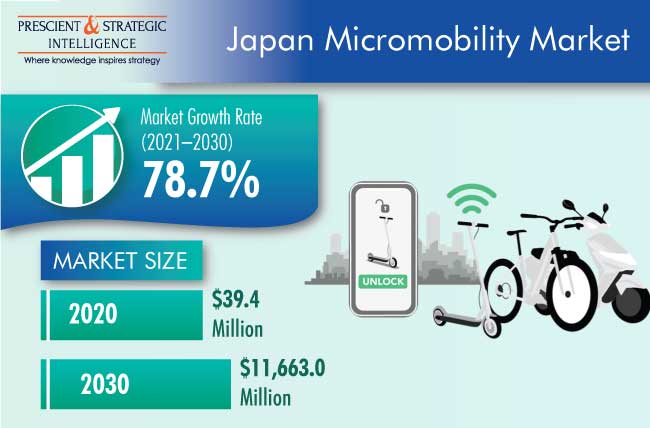
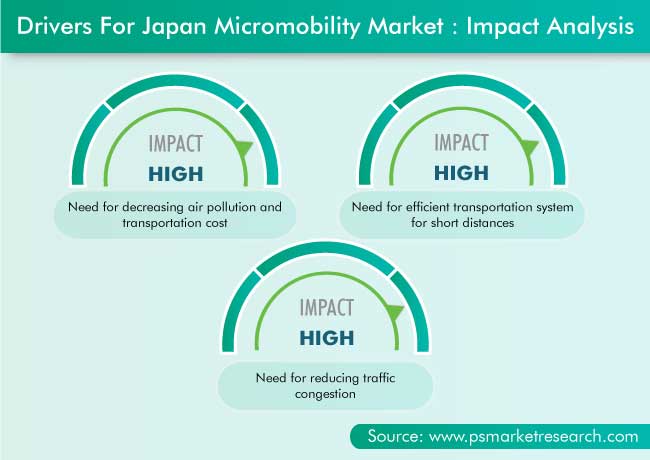
The Japanese micromobility market generated $39.4 million revenue in 2020, and it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 78.7% during the forecast period (2021–2030). The key factors responsible for the growth of the market, include the surging need for decreasing air pollution and transportation cost, efficient transportation system for short distances, and reducing traffic congestion.
The COVID-19 infection has stepped into almost every country across the world, including Japan. It has significant impact on the overall shared mobility and transportation industry. The use of shared vehicles, such as e-scooters, bicycles, and cars, facilitate physical distancing, however, the risk of contagion due to the contact of different users with the same surfaces has discouraged their use. Therefore, many players and operators have had to shut down their operations. As the country fights with COVID-19, the industry is expected to witness more holistic policies that integrate mobility across modes, encouraging multimodality and complementary services. This is expected to increase their demand in coming years.
E-scooters category to witness fastest growth, due to convenient mode of transportation
The e-bikes category dominated the micromobility market in Japan during the historical period, on the basis of vehicle type. This is mainly due to the fact that e-bike sharing service is a convenient and environment-friendly mobility option, which is extremely beneficial in curtailing the problem of pollution. Also, e-bikes are widely adopted by younger generation due to their advanced features. Whereas, the e-scooters category is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period. This will be mainly due to the economical in nature over other predominant public transportation options, and growing fleet size and promising contribution of e-scooter sharing service to solve the problem of last- and-first mile connectivity.
Dockless category to witness faster growth, due to cost efficiency and convenient features
The dockless category is expected to register faster growth in the Japanese micromobility market during the forecast period, based on sharing system. This can be attributed to the rising number of companies opting for dockless bike sharing concept, as it requires less expenditure than a docked system. The users find dockless bike sharing more attractive, due to its cost efficiency and convenient features, such as easy and flexible parking.
Adoption of battery swapping technology for charging micromobility fleet is a key market trend
The introduction of swappable batteries has increased the fleet uptime substantially, and also reducing operational costs, which has ultimately taken the micromobility industry in Japan toward profitability. Additionally, with the use of swappable batteries, revenue generation can be improved, as it not only cuts a large part of the charging costs, but also advances the vehicle availability. The swapping of batteries can be achieved in two ways: (a) The rider replaces the discharged battery with a charged one at a dedicated swapping center. (b) A micromobility employee or freelancer goes around the city and swaps discharged batteries with charged ones.
Need for decreasing transportation cost is key market driver
The growth of the micromobility ecosystem has been exponential, due to factors such as high availability, low pricing, and ease of functioning. The rise in adoption rate of micromobility services has been 10 times higher as compared to the ride-sharing services in its initial phase. Most lucrative criteria for selecting a service for a consumer is cost. Micromobility offers a low-cost travel option, which has lured commuters to try the service for the first time. Along with cost saving, micromobility can also save time of travel, due to its compact and swift nature. The option of low-cost commute also motivates the consumers to replace their walking phase with a suitable mode for first- or last-mile connectivity. Further, the government has also identified micromobility as a replacement to intra-city transportation systems during the peak hours. Thus, these factors driving the Japanese micromobility market growth.
Need for efficient transportation system for short distances boosting the market growth
The need for efficient transportation system for the first- and last-mile connectivity becomes more pertinent, due to the large population base, traffic congestion, increase in price of vehicles, and less availability of parking space. This offers an ample opportunity for service providers operating in the Japanese micromobility market. The transit options for short distances include e-bikes, e-scooters, cycles, skates, e-rickshaws, and shared pods. One of the most popular methods of this transit mode is dockless bike sharing system, which allows users to book a bicycle online through an app and go to any nearest parked bike with the help of GPS and use it. After reaching the destination, instead of having to park the bike in a particular kiosk, the user can leave the bike at any nearby parking area and pay for the service online. Several startups such as Ofo, Mobike, and Nextbike are operating based on this concept in the country.
| Report Attribute | Details |
Historical Years |
2019-2020 |
Forecast Years |
2021-2030 |
Base Year (2020) Market Size |
$39.4 Million |
Market Size Forecast in 2030 |
$11,663 Million |
Forecast Period CAGR |
78.7% |
Report Coverage |
Market Trends, Drivers, and Restraints; Revenue Estimation and Forecast; Segmentation Analysis; Impact of COVID-19; Companies’ Strategic Developments; Company Profiling |
Market Size by Segments |
By Vehicle Type; By Model; By Sharing System |
Secondary Sources and References (Partial List) |
Alternative Fuels Data Center (AFDC); Electric Drive Transportation Association (EDTA); Electric Vehicle Association of Asia Pacific (EVAAP); International Energy Agency (IEA); International Kicksled and Scooter Association (IKSA); International Scooter Association (ISA); Land Transport Authority (LTA); Light Electric Vehicle Association (LEVA); Mobility as a Service Alliance (MaaS Alliance); Shared Active Transportation (SAT) |
Explore more about this report - Request free sample
Market players involved in expansion to gain significant position
In recent years, the players in the Japanese micromobility market have been involved in expansion, in order to attain a significant position in the market. For instance:
- In March 2019, WIND Mobility Ltd. expanded its operations at Urawa-misono station in Saitama city of Japan, with a fleet of 10 e-scooters. These scooters have maximum speed up to 19 km per hour and cost $1.0 for unlocking and $0.25 per minute thereafter.
- In the end of 2019, Docomo Bike Share Co. Ltd., a bike sharing company based in Japan, expanded its service with around 13,400 bikes and 1,660 docking stations in 30 locations across Japan. Further, the company is planning to extend the use of its services by improving accessibility, to clean up the environment, through collaborations with partners in coming years.
Key Players in Japan Micromobility Market Include:
-
Mobby ride Inc.
-
Hasegawa Kogyo Co. Ltd.
-
EXx Co. Ltd.
-
OpenStreet Inc.
-
Segway Inc.
-
NAVITIME JAPAN Co. Ltd.
-
Docomo Bike Share Co. Ltd.
-
Mobike
Market Size Breakdown by Segments
The Japanese micromobility market report offers comprehensive market segmentation analysis along with market estimation for the period 2019-2030.
Based on Type
- E-scooters
- E-bikes
- E-mopeds
- E-pods
- Bikes
- Scooters
Based on Model
- First- and Last-Mile
- Multimodal
Based on Sharing System
- Docked
- Dockless
In 2030, the value of the Japanese micromobility market will be $11,663.0 million.
The Japanese micromobility market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 78.7% during the forecast period (2021–2030).
E-bikes are the largest category under the vehicle type segment of the Japanese micromobility industry.
The major Japanese micromobility market drivers include the need for decreasing air pollution and transportation cost, requirement for efficient transportation system for short distances, and necessity for reducing traffic congestion.
Most Japanese micromobility market players are adopting the strategy of expansion to sustain their business growth.
Want a report tailored exactly to your business strategy?
Request CustomizationWant an insight-rich discussion with the report author?
Speak to AnalystOur dedication to providing the most-accurate market information has earned us verification by Dun & Bradstreet (D&B). We strive for quality checking of the highest level to enable data-driven decision making for you
Our insights into the minutest levels of the markets, including the latest trends and competitive landscape, give you all the answers you need to take your business to new heights
With 24/7 research support, we ensure that the wheels of your business never stop turning. Don’t let time stand in your way. Get all your queries answered with a simple phone call or email, as and when required
We take a cautious approach to protecting your personal and confidential information. Trust is the strongest bond that connects us and our clients, and trust we build by complying with all international and domestic data protection and privacy laws