Hospital-Acquired Infection Control Market Future Prospects
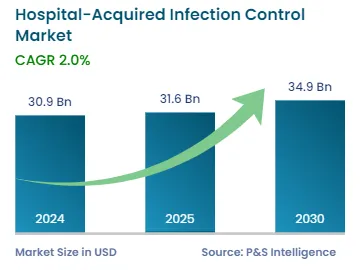
The global hospital-acquired infection control market will generate an estimated revenue of USD 30.9 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 2.0% from 2024 to 2030, reaching USD 34.9 billion by 2030. This is due to the increasing number of surgical procedures, growing awareness of environmental & personal hygiene, and subsequent growth in the prevalence of chronic diseases.
All hospitalized patients are susceptible to contracting a nosocomial infection. Young children, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems are all more susceptible to hospital infections than others. The major risk factors for the infections include long hospital stays, use of indwelling catheters, failure of healthcare staff to wash their hands, and overuse of antibiotics. Also, HAIs kill more people each year globally than car accidents, breast cancer, or AIDS. Thus, there is an utmost necessity to control HAIs.
Moreover, COVID 19, has made consumers more aware of the need to maintain hygiene, at a personal level as well as in public places, to reduce the chances of infection.
The rate of HAIs significantly increased during the pandemic, with the rise in nursing hours. During the period, the medical device-related infections, catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs), and central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) were also increased, due to the change in the complexity of hospitalized patients and safety practices that were implemented to decrease virus transmission risk to healthcare providers. Thus, the control measures were taken at a very higher pace, which impacted the hospital-acquired infection control market positively during the pandemic time.