Report Code: 12013 | Available Format: PDF | Pages: 130
Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Research Report: By Technology (Cadmium Telluride, Copper Indium Gallium Diselenide, Gallium Arsenide), Grid Type (On-Grid, Off-Grid), Application (Building-Mounted, Automotive, Aerospace) - Global Industry Analysis and Growth Forecast to 2030
- Report Code: 12013
- Available Format: PDF
- Pages: 130
- Report Description
- Table of Contents
- Market Segmentation
- Request Free Sample
Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) To Be Most Widely Adopted Technology in Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market
The global ultra-thin solar cells market valued $30.0 million in 2019, and it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 56.9% during the forecast period (2020–2030). The declining prices of such photovoltaic (PV) panel components and rising demand for renewable energy are the key factors driving the advance of the industry around the world.

Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Segmentation Analysis
The cadmium telluride (CdTe) category, under segmentation by technology, is predicted to continue leading the ultra-thin solar cells market till 2030. This is because, in terms of cost and power generation efficiency, it is the only technology which currently rivals crystalline silicone (c-Si) PV cells. Besides, the other technologies are still in the testing phase, therefore witness extremely low usage.
During the forecast period, the on-grid category, on the basis of grid type, would experience the fastest growth in the ultra-thin solar cells market, as the grid connectivity across the world, save for certain developing and underdeveloped nations, is quite good and on-grid cells offer numerous advantages over the off-grid variants. In on-grid systems, the electricity grid acts as a battery, helping in situations where users require external power; contrary to this, an off-grid system can only run on the energy generated from sunlight.
The building-mounted classification, based on application, held the largest share in the ultra-thin solar cells market in 2019. This is attributed to the fact that such energy generating devices are widely installed on commercial and residential units. Further, owing to their low weight, these PV cells are ideal for roofs, which cannot bear too much load, which leads to their high integration in buildings.
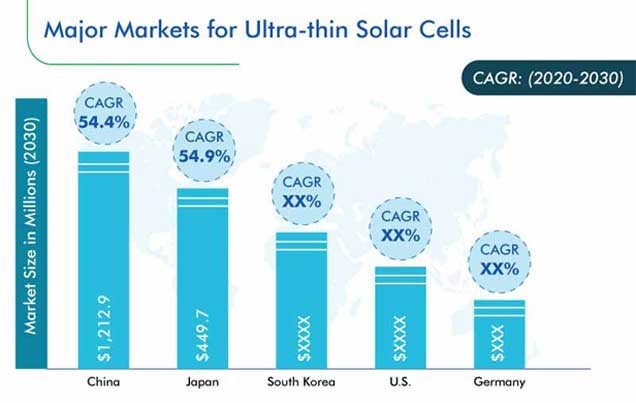
Asia-Pacific (APAC) currently contributes the highest revenue to the ultra-thin solar cells market, as the regional manufacturers of PV panels are engaging in research and development (R&D) to improve their efficiency and bring down their purchase cost, while still making a profit. These efforts have led to the development of ultra-thin solar cells, which are already being used by a number of automakers in the region to manufacture solar-powered electric vehicles (EVs). Thus, due to the robust R&D being carried out by the manufacturers as well as end users of such products, the market is witnessing healthy growth in APAC.
R&D Activities are the Key Trend in the Market
The most prominent trend currently being witnessed in the ultra-thin solar cells market is the increasing number of R&D projects being undertaken around the world. These devices can produce only up to 75% electricity compared to conventional PV cells of equal surface area. Further, the technology has displayed 30% energy efficiency under trials, but it is only 15% efficient on a commercial scale. Thus, to overcome these limitations and reduce their costs, research is being conducted. For instance, in 2019, a semiconductor layer, merely 205 nanometer (nm) thick, was developed together by Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies (C2N) and Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems. Consisting of gallium arsenide (GaAs) on a nanostructured back mirror, this cell displayed 20% energy generation efficiency.
| Report Attribute | Details |
Historical Years |
2014-2019 |
Forecast Years |
2020-2030 |
Market Size by Segments |
Technology, Grid Type, Application |
Market Size of Geographies |
U.S., Canada, Germany, France, U.K., Italy, Spain, China, Japan, South Korea, India, Brazil, Saudi Arabia, U.A.E. |
Explore more about this report - Request free sample
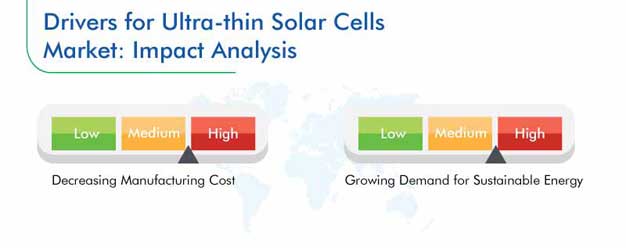
Declining Manufacturing Cost Is an Important Driver for the Market
Among the most important growth drivers for the ultra-thin solar cells market is the decreasing cost of manufacturing such devices. The purchase price of the PV cells is a major factor which decides the cost at which solar electricity is finally sold to customers. Though the levelized cost of energy (LCoE) of PV panels is less than other renewable sources, it is considerably higher than fossil fuels. The International Energy Agency (IEA) says that the LCoE will be $55.7 per Megawatt-hour (MWh) for coal and $66 per MWh for PVs by 2020, equal by 2024, and $57.3 per MWh for coal and $40.0 per MWh for PVs by 2040. This slump in the prices would be driven by R&D, which is aimed at bettering the efficiency and lowering the purchase price of ultra-thin solar cells.
Low-Load-Bearing Buildings and Premium End Users Offer Lucrative Opportunities
A vast growth potential for the ultra-thin solar cells market rests with low-load-bearing buildings and high-end users of such devices, such as the aerospace, automotive, and spacecraft sectors. Compared to conventional, silicon-based PV cells, ultra-thin variants are considered a better alternative, because of their environment-friendly and cost-effective nature. Moreover, they are able to produce a high power output, relative to their weight, which is why they are ideal for automobile batteries and other such auxiliary energy storage devices, spaceship and aircraft power plants, sensors and actuators in soft robotics, and wearable electronics. Similarly, to reduce the weight on the rooftops, several buildings with a low load bearing capacity have integrated ultra-thin solar cells.
Client Wins Are Shaping the Competition in the Market
In recent years, numerous companies in the ultra-thin solar cells market have successfully won orders and commissioned their products, to help build brand image and customer trust.
For instance, in April 2019, Stadtwerke Waldkirch GmbH, a client of SunMan (Hong Kong) Ltd., commissioned a PV system, with a nominal output of 245 kilowatts (kW), on the rooftop of one of its office buildings in Germany. The PV system consists of lightweight, ultra-thin, glass-free crystalline modules supplied by SunMan (Hong Kong) Ltd. After this commissioning, SunMan also planned to introduce the product in other countries in Europe.
On similar lines, in December 2017, the eArche solar panels provided by SunMan (Hong Kong) Ltd. were installed on Byron Bay’s first solar train. Converting sunlight to electricity via the 6.4 kW eArche solar panels and storing it in a large battery, the train, which also had a diesel locomotive for emergency traction support, operated completely on clean energy.
Major players in the global ultra-thin solar cells market are SunMan (Hong Kong) Ltd., Flisom AG, Antec Solar GmbH, MetSolar, Nanosolar Inc., PowerFilm Solar Inc., Swift Solar, AZUR SPACE Solar Power GmbH, and SunFlare.
Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Size Breakdown by Segment
The ultra-thin solar cells market report offers comprehensive market segmentation analysis along with market estimation for the period 2014–2030.
Based on Technology
- Cadmium Telluride (CdTe)
- Copper Indium Gallium Diselenide (CIGS)
- Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)
Based on Grid Type
- On-Grid
- Off-Grid
Based on Application
- Building-Mounted
- Automotive
- Aerospace
Geographical Analysis
-
North America
- U.S.
- Canada
-
Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
-
Asia-Pacific (APAC)
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
-
Rest of the World (RoW)
- Brazil
- Saudi Arabia
- U.A.E
Want a report tailored exactly to your business strategy?
Request CustomizationWant an insight-rich discussion with the report author?
Speak to AnalystOur dedication to providing the most-accurate market information has earned us verification by Dun & Bradstreet (D&B). We strive for quality checking of the highest level to enable data-driven decision making for you
Our insights into the minutest levels of the markets, including the latest trends and competitive landscape, give you all the answers you need to take your business to new heights
With 24/7 research support, we ensure that the wheels of your business never stop turning. Don’t let time stand in your way. Get all your queries answered with a simple phone call or email, as and when required
We take a cautious approach to protecting your personal and confidential information. Trust is the strongest bond that connects us and our clients, and trust we build by complying with all international and domestic data protection and privacy laws